Specification: Body - Bronze, Insert - Tin Made in B.S.P sizes 15mm to 50mm and conforming to Boiler Code Standard No. AS 1732. Standard temperature is 232°C. Suitable for saturated steam pressures up to 1240kPa. Steam pressures in excess of 1240kPa, require plugs 21 to 65°C above the steam temperature.
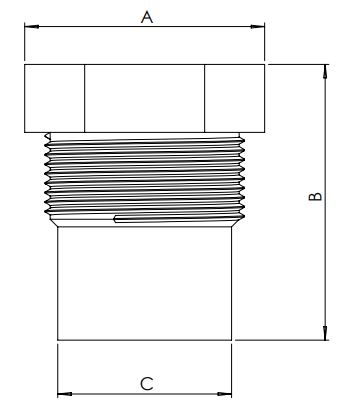
| Model | Size (BSPT) | A (mm) | B (mm) | C (mm) |
| PFS-15 | 1/2" | 22 | 54 | 17 |
| PFS-20 | 3/4" | 29 | 45 | 22 |
| PFS-25 | 1" | 35 | 56 | 25 |
| PFS-32 | 1 1/4" | 44 | 60 | 32 |
| PFS-40 | 1 1/2" | 59 | 62 | 44 |
| PFS-50 | 2" | 64 | 68 | 54 |
-
What is the purpose of a BSP Fireside Bronze Fusible Plug with Tin Insert?
The BSP Fireside Bronze Fusible Plug acts as a crucial safety device in boilers and similar systems. Its primary function is to melt at a specific temperature, allowing it to release built-up pressure. This mechanism prevents boiler or system failures, such as major explosions or accidents, by ensuring that pressure does not exceed safe limits during high-temperature or over-pressurized conditions.
-
What standards does this fusible plug conform to?
This fusible plug is certified to Boiler Code Standard No AS 1732. It meets rigorous safety and performance requirements, ensuring reliable protection and compliance with industry regulations.
-
What is the maximum steam pressure this plug can handle?
The fusible plug is designed to handle saturated steam pressures up to 1240 kPa (approximately 179 psi). For systems operating at pressures higher than 1240 kPa, it is recommended to use plugs with melting temperatures 21 to 65°C above the steam temperature to maintain an adequate safety margin.
-
What is the operating temperature of this fusible plug?
The standard operating temperature for this fusible plug is 232°C (450°F). For applications requiring higher temperatures, custom options are available to meet specific system requirements.
-
Can this plug be used for superheated steam?
This fusible plug is primarily designed for use with saturated steam. If your system operates with superheated steam or has specialized requirements, please consult with our technical support team to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
-
How do I install the fusible plug?
Installation should follow the boiler manufacturer’s guidelines:
- Locate the designated fireside position as specified in the boiler manual.
- Thread the fusible plug into the designated spot using BSP threads.
- Seal the threads properly with thread tape or an approved sealant to ensure a secure and leak-free fit.
- Ensure the plug is tightly secured to function correctly as a safety device.
-
How do I select the right fusible plug for my system?
To select the appropriate fusible plug:
- Determine your boiler’s operating pressure and temperature.
- Choose a fusible plug that matches or exceeds these specifications.
- For steam pressures above 1240 kPa, ensure the plug’s melting temperature is 21–65°C above the steam temperature to provide a sufficient safety margin.
-
What maintenance is required for fusible plugs?
Regular maintenance ensures the fusible plug functions correctly:
- Inspect the fusible plug during routine boiler maintenance.
- Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or melting.
- Replace the plug immediately if any damage or tampering is detected.
- Ensure the plug remains clean and free from obstructions to maintain its effectiveness.
-
What materials are used in this fusible plug?
The fusible plug is constructed from:
- Bronze body: Provides durability and resistance to high temperatures and pressures.
- Tin insert: Serves as the fusible element that melts at the designated temperature to release pressure.
-
Do you offer certifications with the product?
Yes, we provide full material and compliance certificates upon request. Each fusible plug undergoes rigorous testing before leaving our facility to ensure it meets all safety and quality standards.
-
How long will it take to receive my order?
Delivery times vary based on your location and chosen shipping method:
- Express Freight: Typically arrives by the next business day for packages under 5 kg in metropolitan areas of Australia.
- Standard Road Freight: Usually takes 1–10 days, averaging around 3 days, depending on your specific location.
-
What warranty do I get?
Our fusible plugs come with a 12-month warranty. We implement strict quality controls and conduct pre-dispatch testing to minimize any issues. Additionally, our support team is available to assist you post-purchase, ensuring your satisfaction and peace of mind.
-
What is the melting point of a fusible plug?
A typical fusible plug uses a tin alloy with a melting point of 232°C (450°F). This precise melting temperature ensures the plug activates at the correct moment to release pressure and prevent system failure.
-
What metals are used in fusible plugs?
Fusible plugs are commonly made from:
- Bronze
- Brass
- Gunmetal
-
Which types of cylinders use fusible metal plugs and what is their melting temperature?
Fusible metal plugs are often used in acetylene cylinders, specifically in devices like the CG-3. These plugs utilize an alloy with a melting point between 208°F and 220°F (98°C to 104°C), with a nominal melting temperature of 212°F (100°C). They serve as safety mechanisms to release pressure if the cylinder overheats.
-
What is the general purpose of a fusible plug?
Fusible plugs are essential safety components that:
- Maintain the plug’s metal temperature below its melting point under normal conditions.
- Act as fail-safe valves by melting and releasing pressure when abnormal or dangerous temperatures occur.
- Prevent overheating and potential explosions in closed vessels like boilers and cylinders.
-
What happens if a high melting point metal is used as a fuse wire?
Using a conductor with a high melting point in a fuse wire would require excessive heat to melt and interrupt the circuit. This delay can lead to:
- Short circuits
- Fires
- Electrocution risks
-
What is the temperature range of a fusible plug?
Fusible plugs are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges based on their application:
- Historically used plugs operating at 100–110°C (212–230°F). However, due to environmental concerns related to refrigerant gas releases, these functions have largely been replaced by electrical switches.
- Typically operate at higher temperatures as specified by system requirements.
-
How is a fusible plug constructed?
A fusible plug is constructed from:
- Fusible Alloy (Tin Material): Acts as the temperature-sensitive element that melts to release pressure.
- Metal Body (Brass, Bronze, or Gunmetal): Forms a threaded, hollow cylinder with a tapered hole drilled completely through its length.
-
What materials are found inside a fusible plug?
Inside a fusible plug:
- Tapered Hole: Drilled completely through the length of the metal cylinder.
- Low-Melting-Point Metal (e.g., Tin): Seals the tapered hole and is designed to melt and flow away when exposed to high temperatures, enabling the plug to release pressure.
-
What is the difference between a fusible plug and a ruptured disc?
While both fusible plugs and rupture discs serve as safety devices to release pressure, they operate differently:
- Fusible Plugs:
- Material-Based Activation: Made from metals that melt at specific temperatures.
- Gradual Pressure Release: Activate when the temperature exceeds a set point, allowing pressure to be released gradually.
- Used in Systems Requiring Temperature-Based Safety: Such as boilers and certain cylinders.
- Rupture Discs:
- Membrane-Based Activation: Consist of a thin membrane designed to burst at a predetermined pressure.
- Immediate Pressure Release: Provide a rapid and complete release of pressure once the burst occurs.
- Used in Systems Requiring Pressure-Based Safety: Such as chemical processing and high-pressure storage systems.
If you have any further questions or need assistance in selecting the right fusible plug for your application, feel free to contact our support team. We're here to help ensure your systems operate safely and efficiently.
- Fusible Plugs:
| SKU | PFS |
| Brand | Stead and Baker |
Help other Stead & Baker users shop smarter by writing reviews for products you have purchased.